Which mesh simplification methods are available?
Convex Hull
This algorithm simplifies the object 3D by a convex hull and has no parameters. The left picture is the original object, the right picture is the simplified object, approximated by a convex hull.
| Original mesh | Convex hull |
|---|---|
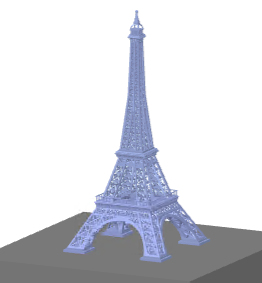 |
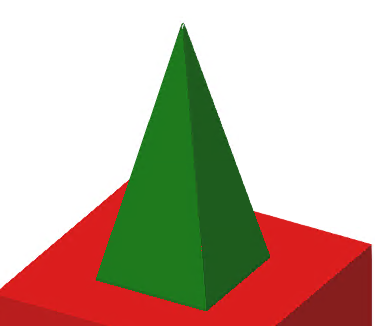 |
Bounding Box
This algorithm simplifies the 3D object by those bounding box and has no parameters. The left palett is the original object, the palett on the right-hand side is the simplified object.
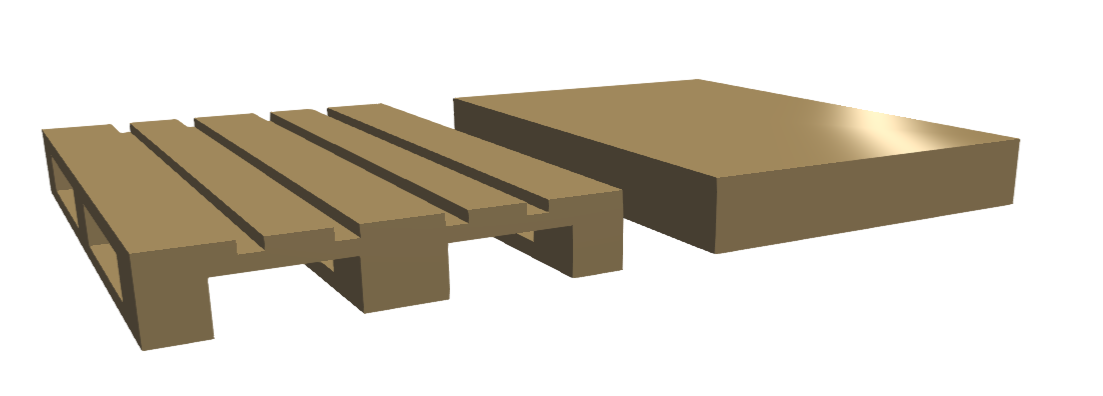
Convex Decomposition
twin provides two convex decomposition algorithms to approximate a concave object with convex ones.
The first algorithm (VHCD2) has more parameters than the newer one (VHACD4) which offers more influence to the user on the parameterization but is much slower regarding the decomposition process.
VHACD2
| Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha | 0.05 | Controls the bias toward clipping along revolution axes. Range: 0.0-1.0 |
| Beta | 0.0001 | Controls the adaptive sampling of the generated convex-hulls. Range: 0.0-1.0 |
| Convex hull down-sampling | 4 | Controls the precision of the convex-hull generation process during the clipping plane selection stage. Range: 1-16 |
| Convex hull approximation | TRUE | |
| Maximum allowed concavity | 0.001 | Range: 0.0-1.0 |
| Max allowed convex hulls | 1024 | |
| Max vertices per convex hull | 64 | Controls the maximum number of triangles per convex-hull. Range: 4-1024 |
| Min volume per convex hull | 0.0001 | Range: 0.0-1.0 |
| PCA | TRUE | Enable/disable normalizing the mesh before applying the convex decomposition. |
| Plane down-sampling | 4 | Controls the granularity of the search for the "best" clipping plane. Range: 1-16 |
| Project hull vertices | TRUE | If set to true, this will project the output convex hull vertices onto the original source mesh to increase the floating point accuracy of the results |
| Resolution | 100000 | Maximum number of voxels generated during the voxelization stage. Range: 10000-64000000 |
The parameters that have the most influence in the decomposition are:
- Convex hull approximation
- Project hull vertices
- Resolution
Example
Original:
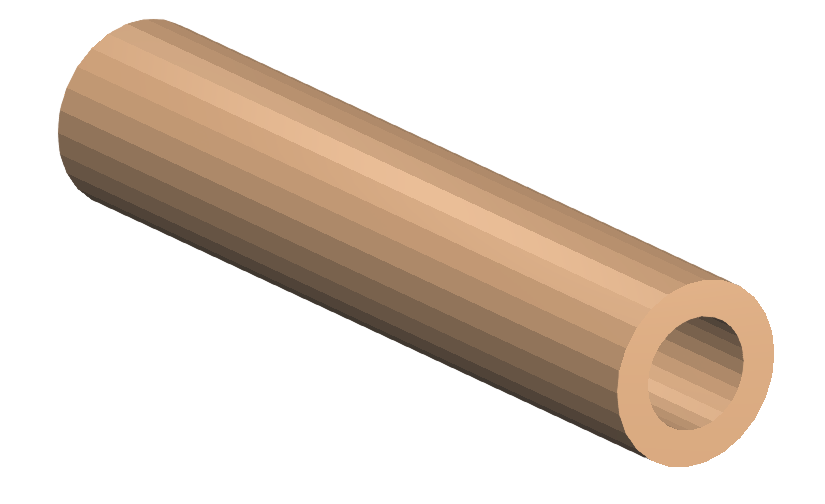
Decomposition 1:
Parameters:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Convex hull approximation | TRUE |
| ProjectHullVertices | TRUE |
| Resolution | 1E5 |
Result:
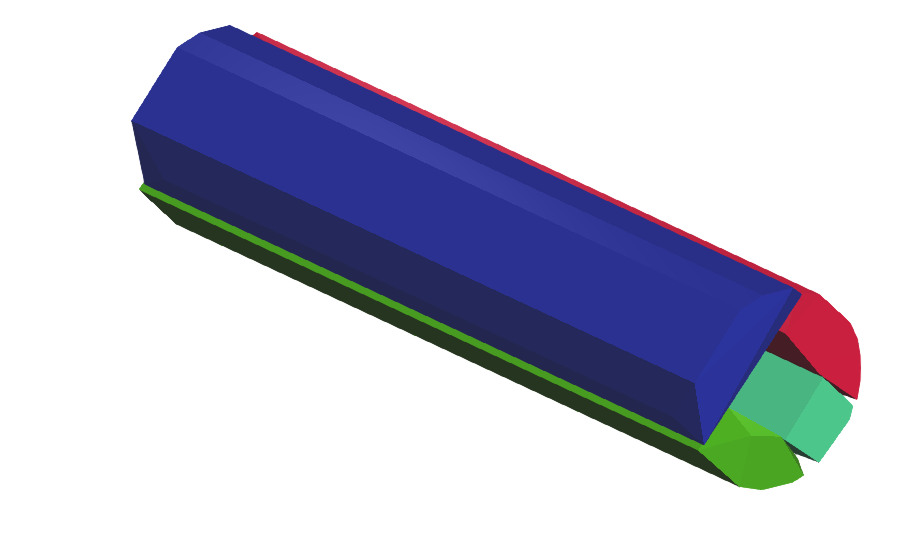
Decomposition 2:
Parameters:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Convex hull approximation | FALSE |
| ProjectHullVertices | FALSE |
| Resolution | 1E6 |
Result:
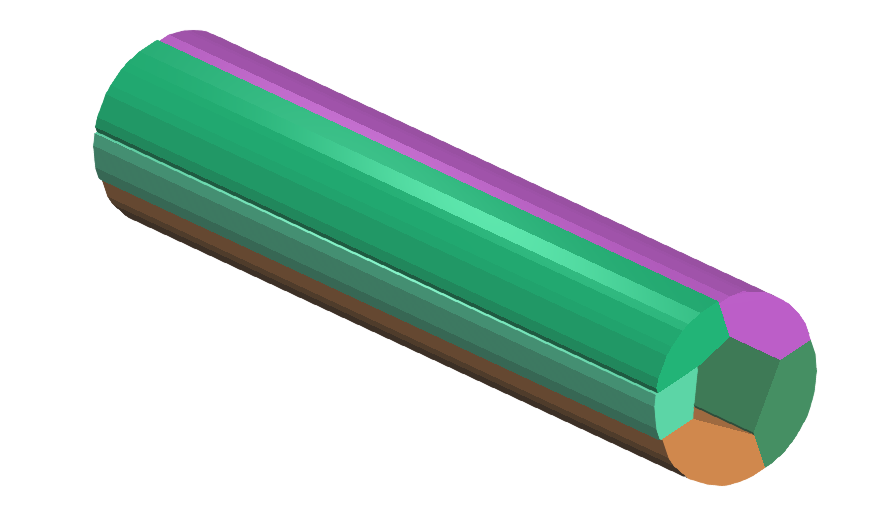
Decomposition 3:
Parameters:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Convex hull approximation | FALSE |
| ProjectHullVertices | FALSE |
| Resolution | 1E7 |
Result:
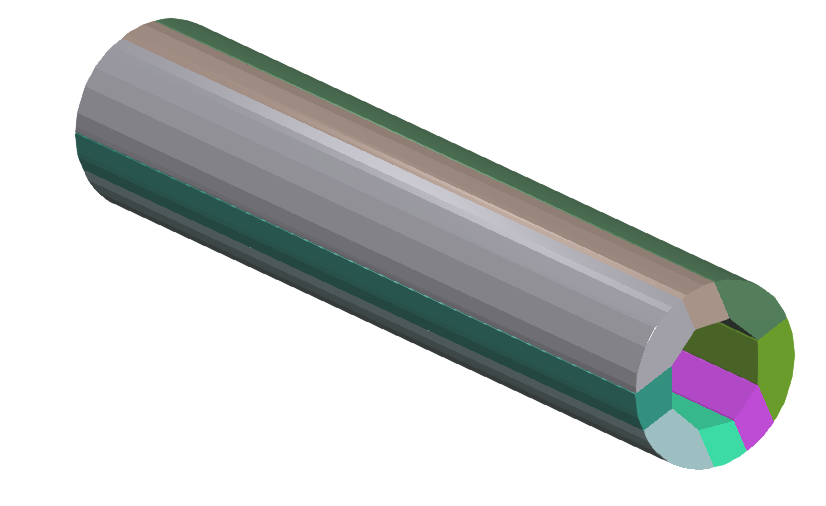
VHACD4
| Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FindBestPlane | FALSE | |
| Maximum convex hulls | 256 | The maximum number of convex hulls the result may have. |
| Maximum vertices per convex hull | 512 | |
| Max recursion depth | 12 | |
| Min edge length | 2 | |
| Minimum volume of convex hulls | 1E-9 | |
| Minimum volume percent error allowed | 0 | |
| Resolution | 400000 | The number of voxels to use. The higher voxel resolution then the more fine details you can capture. |
The parameters that have the most influence in the decomposition are:
- Maximum convex hulls
- Resolution
Example
Original:
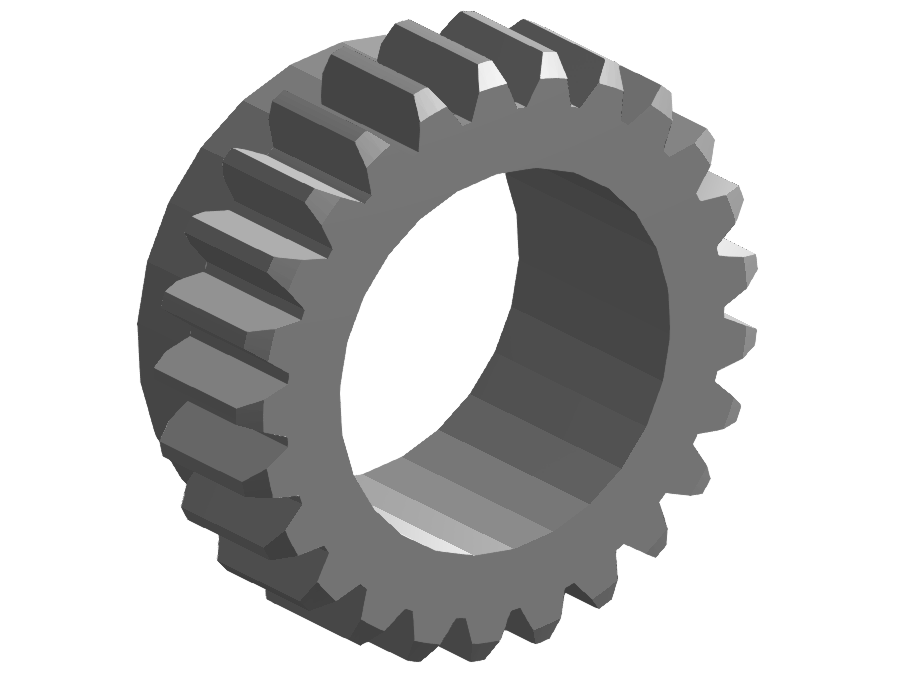

Decomposition 1:
Parameters:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum convex hulls | 256 |
| Resolution | 4E5 |
Result:
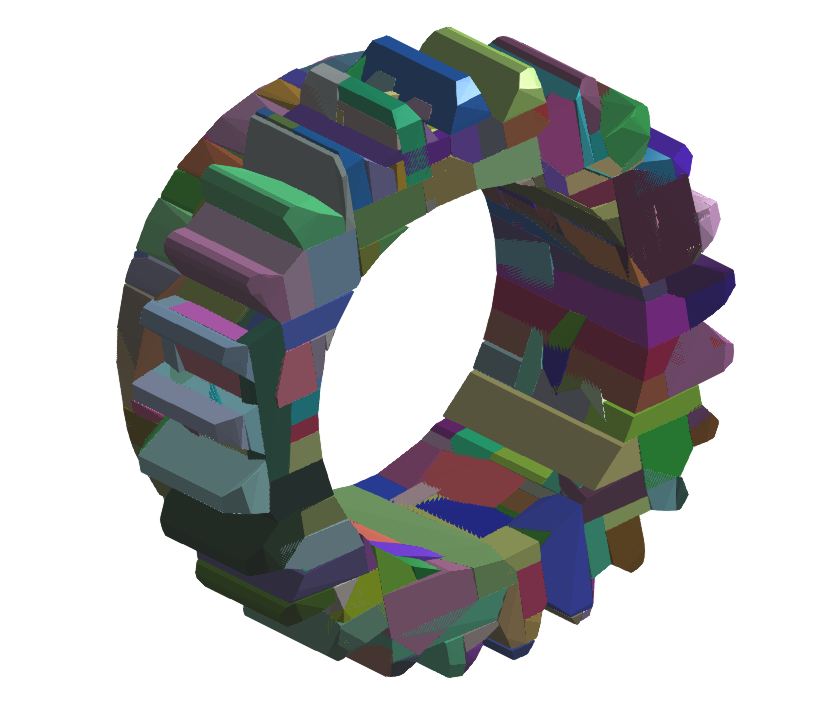
Decomposition 2:
Parameters:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum convex hulls | 1024 |
| Resolution | 1E6 |
Result:
Further Information
For more details visit the Video Guides section, where you can find additional information and video guides on this topic under Simulate complex 3D-Objects in real time.