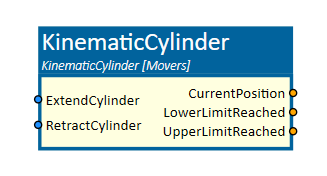
KinematicCylinder
This simulation component moves 3D objects or groups of 3D objects (e.g. a piston rod in terms of a cylinder) along a definable axis and combines cylinder and valve.
When to use
Use this simulation component if you want to move a 3D object (e.g. piston rod of a cylinder) relative to their parents (e.g. housing of a cylinder) along a linear axis. The controlling is done by digital signals depending on the selected mode whether the cylinder should be simulated as MonoStable or BiStable.
How to use
Add this simulation component from the simulation component library. At first select a 3D object or an assembly either in the 3D View window or in the Assembly Structure window using the select button near the property PistonRod.
Then define the translation axis either in the global or in the local coordinate system of the selected 3D object. Define the Mode if the cylinder should be simulated as MonoStable or BiStable.
Finally you can define the TypeOfControlling which indicates whether the 3D object should be translated by setting the speed or the time of the movement.
Parameters
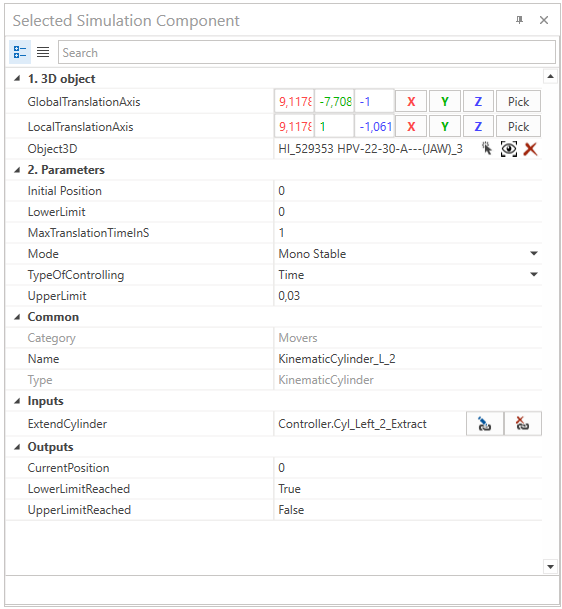
GlobalTranslationAxis
Indicates the translation axis in the global coordinate system.
LocalTranslationAxis
Indicates the translation axis in the local coordinate system of the selected 3D object. You first have to select a 3D object, before you can define the LocalTranslationAxis.
PistonRod
The 3D object which will be translated relative to it's parent. The rigid body behavior of this 3D object and any children must be either None or Kinematic.
InitialPosition
A value in m indicating the initial position of the piston rod.
TypeOfControlling
Indicates if the piston rod of the cylinder gets translated by setting the speed or the time of the movement. Depending on the choice, the property TranslationSpeed or MaxTranslationTimeInS are available to edit.
TranslationSpeed
Indicates the translation speed in m/s. When the translation is controlled by speed, the piston rod moves with this speed. This property is visible if Speed is defined as TypeOfControlling.
MaxTranslationTimeInS
Indicates the translation time in seconds of the translation between upper and lower limit. This property is visible if Time is defined as TypeOfControlling.
Mode
Indicates whether the cylinder should be simulated as MonoStable or BiStable. MonoStable means that the cylinder combined with a valve has only one stable state controlled by one single digital input. If the input ExtendCylinder is set to TRUE, the piston rod moves to the upper limit. If the input is set to FALSE, the piston rod moves to the lower limit.
BiStable means that the cylinder has two stable states controlled by two digital inputs. If the input ExtendCylinder is set to TRUE, the piston rod moves to the upper limit. If the input is set to FALSE, the piston rod stays at this position. If the second input RetractCylinder is set to TRUE, the piston rod moves to the lower limit.
LowerLimit
Indicates the lower limit of the translation in m.
UpperLimit
Indicates the upper limit of the translation in m.
Inputs
ExtendCylinder
An input which moves the piston rod to the upper limit if set to TRUE.
RetractCylinder
An input which moves the piston rod to the lower limit if set to TRUE. This property is visible if the BiStable Mode is defined.
Outputs
CurrentPosition
Outputs a value in m indicating the current position of the translation.
LowerLimitReached
Outputs a value indicating whether the lower limit of the translation is reached or not.
UpperLimitReached
Outputs a value indicating whether the upper limit of the translation is reached or not.
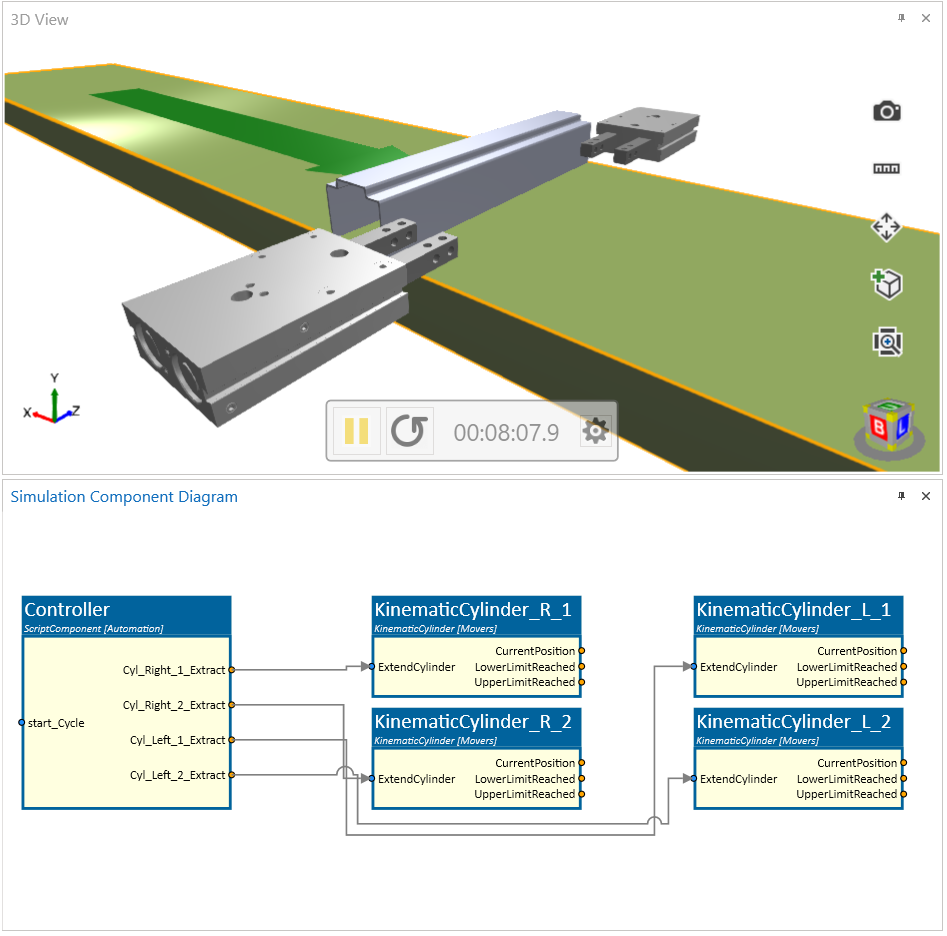
Example
As can be seen in the example above, for each cylinder, the KinematicCylinder component is used. In this case, they are MonoStable. Therefore each of them is controlled by a single output signal from a controller.
The upper limit has been defined by 0.03 m. The selected object 3D moves along the local Y-Axis. Each cylinder is controlled by a time which means that the moving duration from upper to lower limit is in this case one second.
Further Information
For more details visit the Video Guides section, where you can find a video guide demonstrating this topic under Push-off and stopper cylinders.