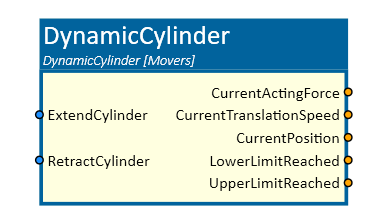
DynamicCylinder
This simulation component translates a dynamic 3D object (e.g. a piston rod of a cylinder) along a definable axis with a definable force and combines cylinder and valve.
When to use
Use this simulation component if you want to move a 3D object (e.g. a piston rod) relative to its parent (e.g. housing of a cylinder) along a linear axis with the defined force. The controlling is done by digital signals depending on the selected mode whether the cylinder should be simulated as MonoStable or BiStable.
How to use
Add this simulation component from the simulation component library.
At first select the 3D object which will be translated. Make that selection either in the 3D View window or in the Assembly Structure window using the select button near the property PistonRod.
Then define the 3D object which should serve as a reference for the movement called Housing.
After that define the translation axis either in the global or in the local coordinate system of the selected PistonRod.
Finally you can define the TypeOfControlling which indicates how the 3D object should be translated e.g. by setting the force of the movement.
The upper and lower limit defines the mechanical limits of the cylinder.
Note
If the dynamic cylinder wobbles or oscillates, you can try to increase the minimum solver iterations for position and velocity.
These values can be found in the Rigid Body Simulation tab in the settings.
Parameters
GlobalTranslationAxis
Indicates the translation axis in the global coordinate system.
LocalTranslationAxis
Indicates the translation axis in the local coordinate system of the selected PistonRod. You first have to select the PistonRod, before you can define the LocalTranslationAxis.
PistonRod
The 3D object which will be translated. The rigid body behavior of this 3D object must be Dynamic.
Housing
The 3D object which serves as a reference for the movement. If this 3D object is empty, the movement is relative to the world.
The rigid body behavior of this 3D object must be either Dynamic, Static or Kinematic.
EnableProportionalOverride
Indicates if the acting force of the PistonRod can get overridden. If enabled, an input is available indicating the override. The used acting force is MaxForce * ProportionalOverride.
TypeOfControlling
Indicates how the PistonRod should be moved by e.g. applying a force.
InitialPosition
A value in m indicating the initial position of the PistonRod.
LowerLimit
Indicates the lower limit of the translation in m.
UpperLimit
Indicates the upper limit of the translation in m.
Mode
Indicates whether the cylinder should be simulated as MonoStable or BiStable. MonoStable means that the cylinder combined with a valve has only one stable state controlled by one single digital input. If the input ExtendCylinder is set to TRUE, the piston rod moves to the upper limit. If the input is set to FALSE, the piston rod moves to the lower limit.
BiStable means that the cylinder has two stable states controlled by two digital inputs. If the input ExtendCylinder is set to TRUE, the piston rod moves to the upper limit. If the input is set to FALSE, the piston rod stays at this position. If the second input RetractCylinder is set to TRUE, the piston rod moves to the lower limit.
MaxForce
Indicates the maximum acting force that the piston rod is allowed to exert.
Inputs
ExtendCylinder
An input which moves the piston rod to the upper limit with the defined force if set to TRUE.
RetractCylinder
An input which moves the piston rod to the lower limit with the defined force if set to TRUE. This property is visible if the BiStable Mode is defined.
ProportionalOverride
An input which overrides the acting force. The used acting force is MaxForce * ProportionalOverride. This property is visible if the EnableProportionalOverride property is enabled.
Outputs
CurrentPosition
Outputs a value in m indicating the current position of the piston rod.
CurrentTranslationSpeed
Outputs a value in m/s indicating the current speed of piston rod.
LowerLimitReached
Outputs a value indicating whether the lower limit of the translation is reached or not.
UpperLimitReached
Outputs a value indicating whether the upper limit of the translation is reached or not.
CurrentActingForce
Indicates the current acting force on the piston rod.
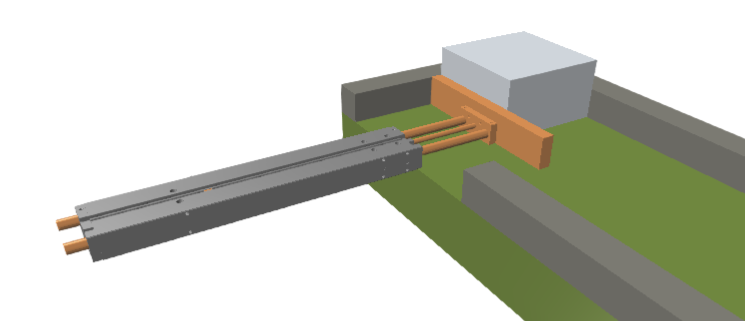
Example
In the following example a cylinder aligns boxes of different sizes by pressing them to a stop. With the KinematicCylinder simulation component, this would not work because with this component, the piston rod always moves to the same position independent to the box size.
The highlighted 3D object is defined as the PistonRod. The housing is also defined.
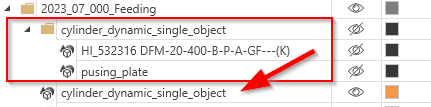
Due to the fact that this simulation component can only move single dynamic 3D objects, a single 3D object has been created
from the grouped components containing e.g. the piston rod and the pushing plate. This can be done by the functionality DuplicateAsSingleObject in the assembly structure.
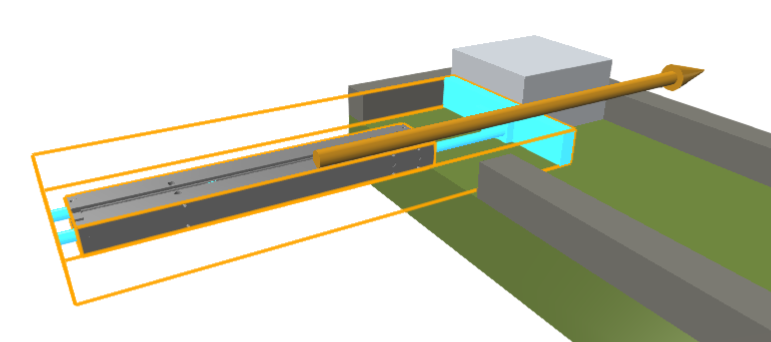
Depending on the mass of the boxes and the single object 3D a MaxForce of 50 N has been defined.
The mechanical limit of the cylinder is at 0.150 m therefore, this has been defined as the upper limit. The initial position of the piston rod is not at the retracted position, therefore, the InitialPosition is also set.
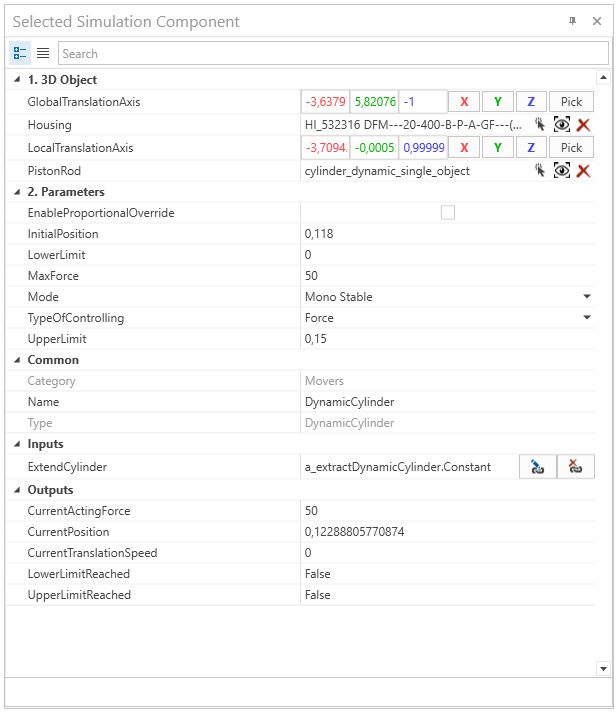
In this case, the Mode MonoStable has been chosen. Therefore the cylinder is controlled by a single output digital signal from a controller.
Further Information
For more details visit the Video Guides section, where you can find a video guide demonstrating this topic under Alignment cylinders.