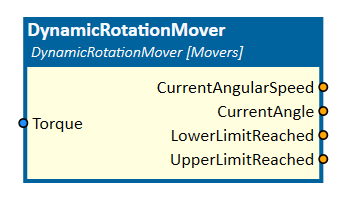
DynamicRotationMover
This simulation component rotates a 3D object by applying a torque.
When to use
Use this simulation component if you want to rotate a 3D object relative to it's parent around an axis. The rotation is done by applying a torque.
With this simulation component you can reconstruct the behavior of each mechanical system which is rotated by e.g. a torque around an axis.
For example, you can use this to control a pendulum in combination with a controller.
To get a better understanding please take a close look to the example down below.
How to use
Add this simulation component from the simulation component library.
At first select the 3D object which will be rotated. Make that selection either in the 3D View window or in the Assembly Structure window using the select button near the property MovingObject3D.
Then define the 3D object which should serve as a reference for the movement called BaseObject3D.
After that define rotation axis and rotation point either in the global or in the local coordinate system of the selected MovingObject3D.
Finally you can define the ControllingType which indicates whether the 3D object should be translated by setting the force or the speed of the movement.
If you are interested in setting an upper and lower limit, you can do that by enabling the specified limits.
Note
If the dynamic mover wobbles or oscillates, you can try to increase the minimum solver iterations for position and velocity.
These values can be found in the Rigid Body Simulation tab in the settings.
Parameters
GlobalRotationAxis
Indicates the rotation axis in the global coordinate system.
LocalRotationAxis
Indicates the rotation axis in the local coordinate system of the selected MovingObject3D. You first have to select the MovingObject3D, before you can define the LocalRotationAxis.
GlobalRotationPoint
Indicates the rotation point in the global coordinate system.
LocalRotationPoint
Indicates the rotation point in the local coordinate system of the selected MovingObject3D. You first have to select the MovingObject3D, before you can define the LocalRotationPoint.
MovingObject3D
The 3D object which will be rotated. The rigid body behavior of this 3D object must be Dynamic.
BaseObject3D
The 3D object which serves as a reference for the movement. If this 3D object is empty, the movement is relative to the world.
The rigid body behavior of this 3D object must be either Dynamic, Static or Kinematic.
ControllingType
Indicates if the MovingObject3D should be moved by applying torque or speed.
InitialPosition
A value in degree indicating the initial position of the MovingObject3D.
LowerLimit
Indicates the lower limit of the rotation in degree. If negative infinite is defined the rotation of the MovingObject3D is not limited.
UpperLimit
Indicates the upper limit of the rotation in degree. If positive infinite is defined the rotation of the MovingObject3D is not limited.
Inputs
Torque
An input indicating the torque in Nm which is applied to rotate the MovingObject3D.
Outputs
CurrentAngle
An output indicating the current angle in rad of the MovingObject3D.
CurrentAngularSpeed
An output indicating the rotation speed in rad/s of the MovingObject3D.
LowerLimitReached
Outputs a value indicating whether the lower limit of the rotation is reached or not.
UpperLimitReached
Outputs a value indicating whether the upper limit of the rotation is reached or not.
Example
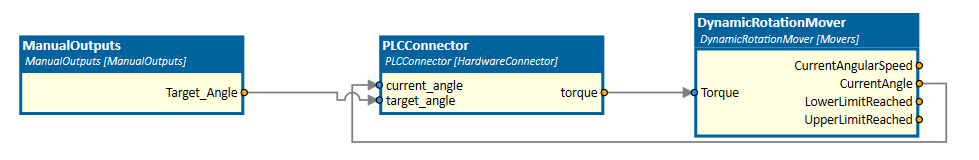
In this example, an angle of a pendulum is controlled by a PLCConnector simulation component as already shown in the picture above.
Therefore the dynamic pendulum object (as seen highlighted in the picture below) is defined as the MovingObject3D of the DynamicRotationMover simulation component.
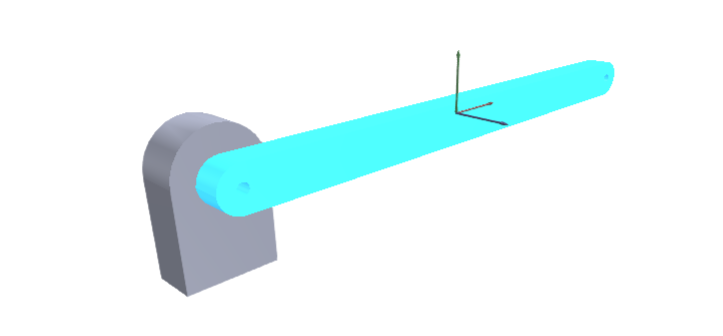
The static base object is defined as the BaseObject3D. As shown in the picture below, the mechanical limits are not set. The positive turning axis is around the negative z-axis (either in the local and global coordinate system).
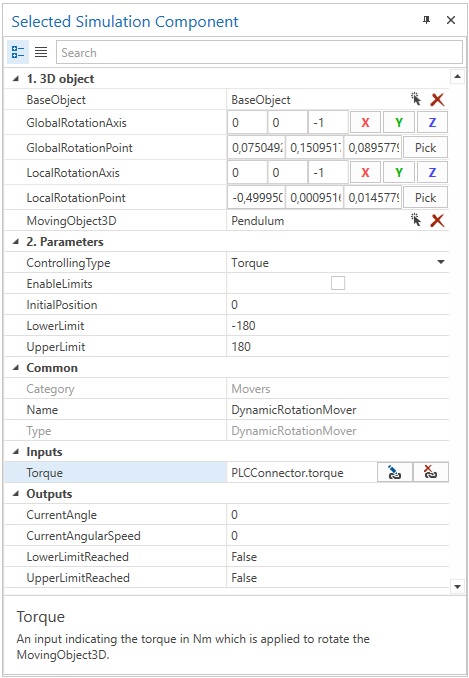
The controller gets the target position which is set manually by the user using the ControlPanel simulation component, receives the current angle of the pendulum from the DynamicRotationMover simulation component and tries to control the angle by the torque.
Further Information
For more details visit the Video Guides section, where you can find a video guide demonstrating this topic under Pivoting cylinder.