Sequence
With this simulation component, you can create a sequence by simply dragging and dropping blocks and use it to control your machine.
When to use
Use this simulation component when you want to control the behavior of a machine using task sequences. This is particularly useful for prototyping automation processes, designing logical flows, or building state machines without programming.
The sequence component is especially suitable for concept studies or simulation scenarios where task-based logic (e.g., waiting for input, setting outputs, moving a robot) needs to be modeled visually and executed during simulation.
How to use
Add this simulation component from the component library. Then define the inputs and outputs the sequence should have.
Now you are ready to visually model the sequence by simply assembling blocks with different tasks such as reading inputs, modifying variables, setting outputs, or moving robots.
Tip
The blocks can be modified during the running simulation. As soon as the "apply button" is pressed, the current arrangement of the blocks is applied. It is like programming a PLC online.
Parameters
AdditionalInputs
The number of inputs the sequence has. You can link these inputs to other simulation components and you can then use the values of the inputs within the sequence by waiting for a specific value or simply reading out the current value.
AdditionalOutputs
The number of outputs the sequence has. You can link these outputs to other simulation components and you can then change the values of the outputs within the sequence.
Sequence
The sequence itself, modeled visually by blocks with different tasks. Use the edit button to open the editor. The sequence is applied after you pressed "apply" within the editor.
Inputs
Inputs are created dynamically according to the defined number of inputs.
Outputs
Outputs are created dynamically according to the defined number of outputs.
Blocks
I/O
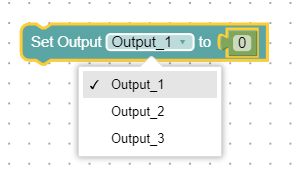
Set Output 'output' to 'value'
This block allows you to select an configured output from a dropdown menu and assign a value to it.
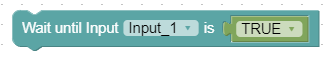
Wait until Input 'input_xy' is 'value'
This block allows you to select a configured input from a dropdown menu. The block completes once the input reaches the specified value.
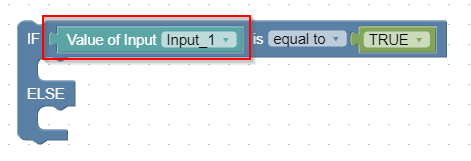
Value of Input 'input_xy'
This block provides the current value of an input. The value can be used as a variable in conditions or assignments.
Robot
Move robot 'robotController' to position 'position'
This block lets you select a robot and a teached position from dropdown menus. It sends a movement command to the robot and waits until the movement is completed.
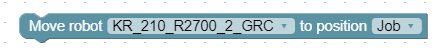
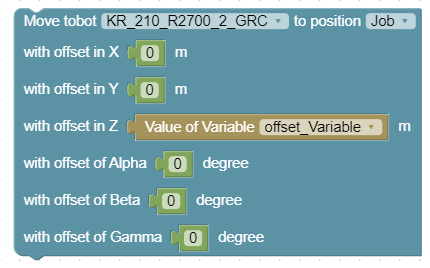
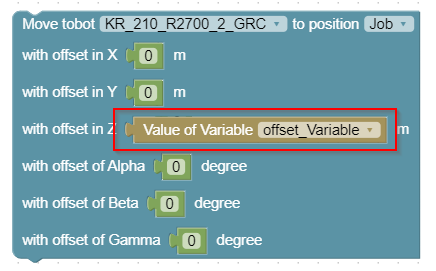
Move robot 'robotController' to position 'position' with offsets
This block lets you select a robot and a teached position from dropdown menus. You can also specify offsets in X, Y, Z or in Alpha, Beta, and Gamma, relative to the robot’s base coordinate system. The block sends the movement command with the offsets to the robot and waits until the movement is completed.
Statements
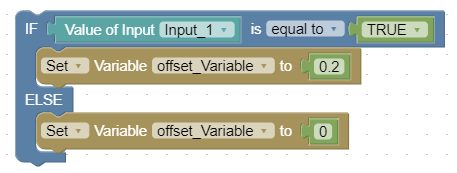
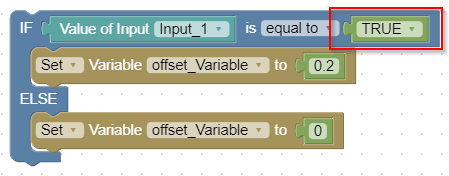
If-Else-Statement
The If-Else block compares two values using various operators (e.g., equal, greater than, less than). If the comparison is true, the "If" branch is executed; otherwise, the "Else" branch runs.
Time
Wait 'value' s
The Wait block allows you to specify a time in seconds. Once the time has elapsed, the block is completed.

Utility
Comment block
The Comment block can be used to add any kind of notes or comments.

Constants
Boolean Constant
This block allows you to specify a boolean constant, either true or false.
Numeric Constant
This block allows you to specify a numeric constant, including values with decimals (floating point).

Variables
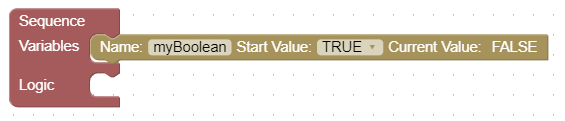
Declaration of a boolean variable
A boolean variable can be created with an optional initial value. This variable can then be used in various blocks to set values or for comparisons.
Declaration of a numeric variable
A numeric variable can be created with an optional initial value. This variable can then be used in various blocks to set values or for comparisons.

Value of a variable 'variableName'
This block allows you to use the current value of the variable, selected via the dropdown, in different blocks for setting values or comparisons.
Editing variable 'variableName' with 'value'
This block enables you to modify the value of a variable—for example, setting it to a specific value, adding or subtracting a value, dividing, or multiplying it.

Example
In this example, a simple sequence using blocks is shown, in which a box is conveyed forward on a conveyor belt and then picked up and stacked by a robot.
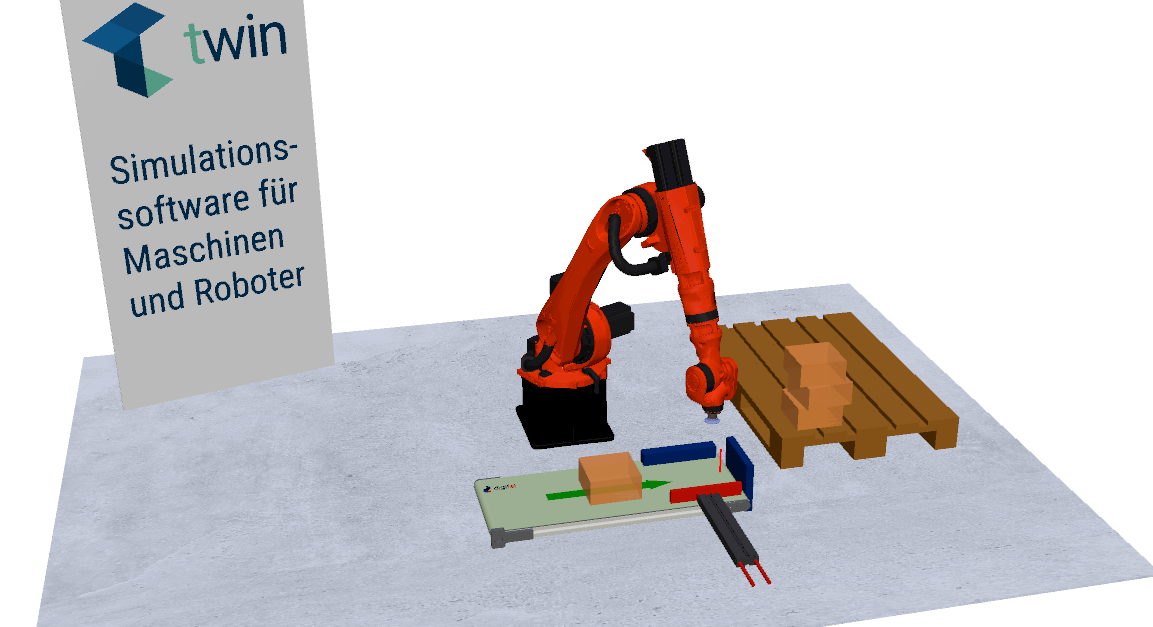
As soon as the light barrier is interrupted and a delay time has elapsed, the box is aligned by a cylinder. After alignment, the box is picked up and stacked by a robot. The stacking pattern is generated dynamically after each cycle based on the declared variable, as this variable is used as an offset.
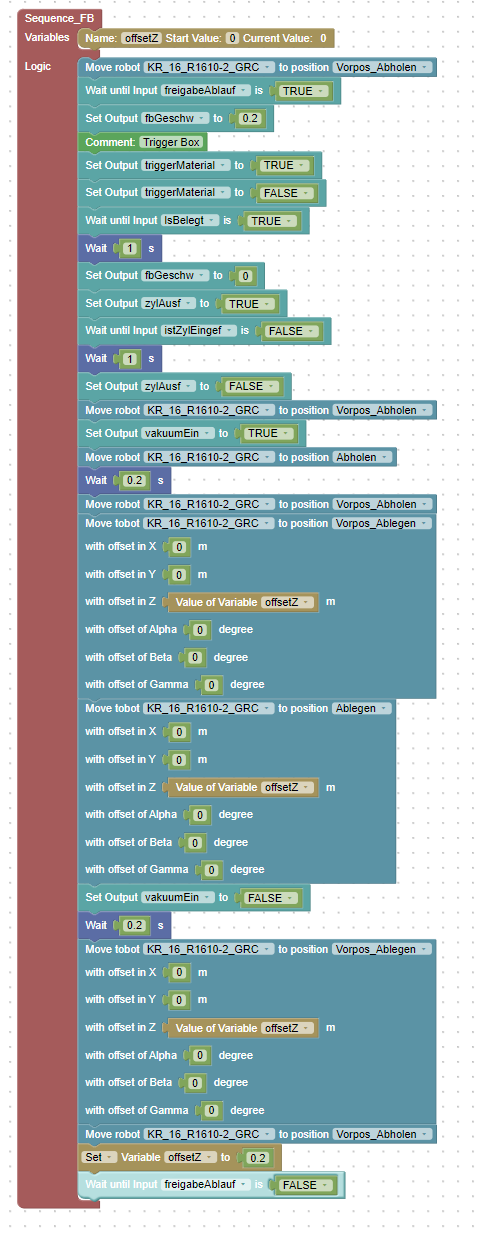
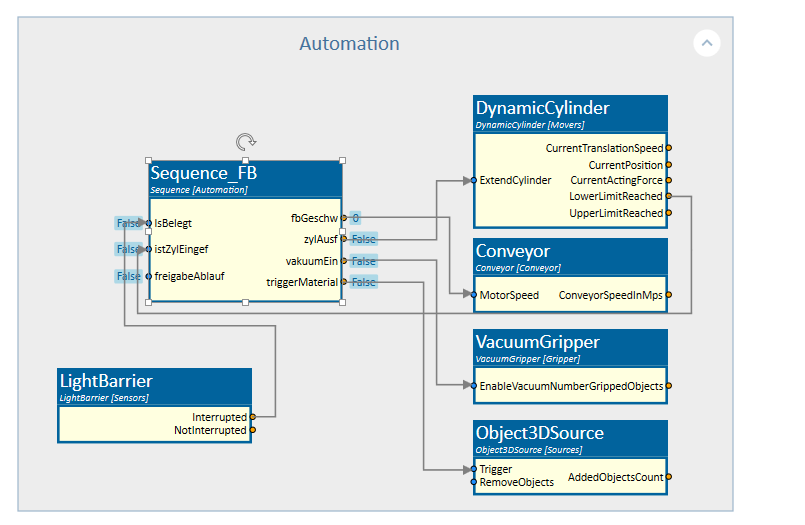
The following image shows the component diagram. It illustrates how the sequence communicates with the actuators and sensors.
One output directly controls the conveyor belt. Another output is responsible for extending the cylinder. A separate output triggers the source of the box, and another activates the vacuum at the gripper. Additionally, there is feedback from the cylinder sensor indicating whether the cylinder is retracted, as well as from the sensor detecting whether the box has reached the front.
The sequence is manually triggered.
Further Information
For more details visit the Video Guides section, where you can find a video guide demonstrating this topic under Graphical programming of sequences.